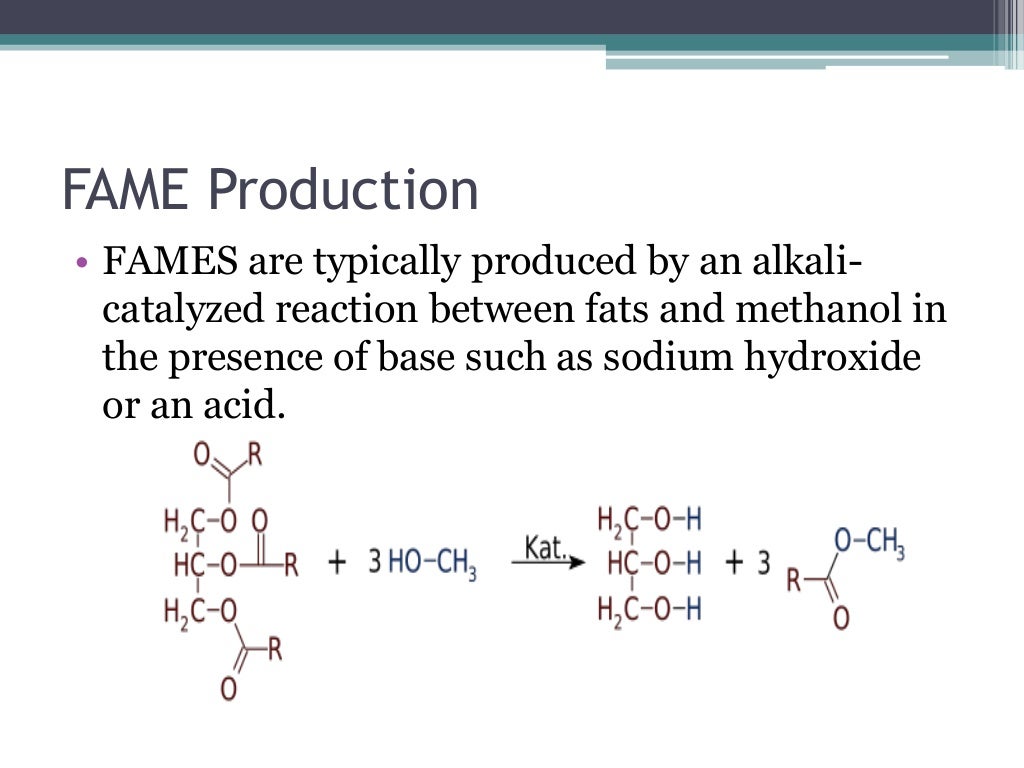
Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids . soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. fat molecules contain three ester links. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). The mechanism of saponification is: These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids.
from dxottdgrn.blob.core.windows.net
saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The mechanism of saponification is: The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives:
A Mixture Of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters at Sheila Hill blog
Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. The mechanism of saponification is: fat molecules contain three ester links. saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its.
From www.researchgate.net
Esterification of free fatty acids and transesterification of a Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.mdpi.com
Molecules Free FullText Synthesis of the Fatty Esters of Solketal Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. the modern. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From exontlwzj.blob.core.windows.net
Fatty Acid Ester Chemical Formula at Cathy Pierce blog Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.researchgate.net
Fattyacids' chemical structures. Download Scientific Diagram Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. The mechanism of saponification is: the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. The ester functional groups are. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From abdel-mawgoud.com
Fatty acid analysis (GCFID) AbdelMawgoud Synthetic Biology Lab Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids fat molecules contain three ester links. saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.mdpi.com
Molecules Free FullText Synthesis, Quantification, and Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. The mechanism of saponification is: fat molecules contain three ester links. after purification to remove. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.chemistrystudent.com
Esters (ALevel) ChemistryStudent Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. The mechanism of saponification is:. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.researchgate.net
Composition of fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) produced from palm oil Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. The mechanism of saponification is: soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). after purification to. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.myxxgirl.com
Reaction Scheme Depicting The Synthesis Of The Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. The mechanism of saponification is: soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). In chemistry, saponification is. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DIETARY FATS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5730225 Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. fat molecules contain three ester links. soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. . Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Ester Chemistry List Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The mechanism of saponification is: fat molecules contain three ester links. saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. the modern definition. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From cmp.krohne.com
KROHNE Fatty acid methyl ester Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. The mechanism of. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.researchgate.net
List of fatty acid esters synthesized and evaluated for oviposition Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids fat molecules contain three ester links. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. The mechanism of saponification is: In chemistry, saponification is defined as the.. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
Fischer Esterification Carboxylic Acid to Ester Under Acidic Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. soap is made by treating fats with. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.researchgate.net
Fatty acids identified as methyl esters in Alternaria sp. Download Table Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids saponification is an alkaline hydrolysis process by which neutral fats (triglycerides) break into glycerol and fatty acids. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium and potassium salts. The mechanism of saponification is: fat molecules contain three ester links. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.academia.edu
(DOC) Determination of Saponification, Acid and Ester Values Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids The mechanism of saponification is: the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: soap is made by treating fats with a strong solution of lye (naoh). These can be hydrolysed when they are heated with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. soaps are long chains of fatty acid sodium. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From www.numerade.com
H) Soaps can be described as (2pts) A) esters of fatty acids B) salts Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids fats and oils can participate in a variety of chemical reactions—for example, because triglycerides are esters, they can be. fat molecules contain three ester links. The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. saponification is the alkaline hydrolysis of the fatty acid esters. These can be hydrolysed when they are. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.
From thebiologynotes.com
Fatty Acids Definition, Classification, Types, Functions Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids In chemistry, saponification is defined as the. the modern definition of soap relates to cleansing agents derived from fats, oils, and other fatty derivatives: The ester functional groups are hydrolyzed releasing its. after purification to remove phospholipids and sterols, fats and oils are treated with alkali to produce soap which is acidified with inorganic. saponification is the. Soaps Can Be Described As Esters Of Fatty Acids.